Comparing Peira TM900 and caliper measurement for tumor volume calculation using a tumor volume formula.
TM900 3D measurement

3D Peira TM900 measurement
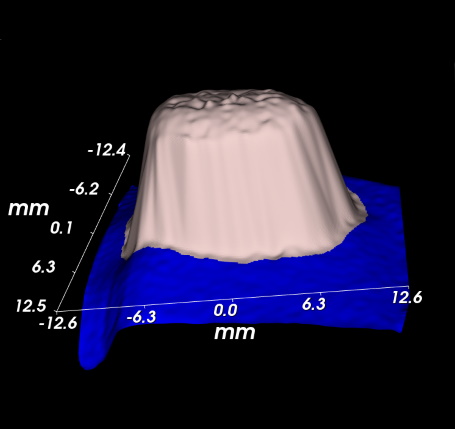
A direct 3D instrument, such as the Peira TM900, will make a stereographic image of the tumor and reconstruct the tumor topography and shape. A direct and real 3D volume of the xenograft will then be calculated.
Monitoring tumor volume through a direct 3D measurement will include changes in all three directions, height, width and length thus resulting in more accurate realistic data.
With constant width and length, the volume changes with the shape of the tumor. The obtained data include height and topography variations.
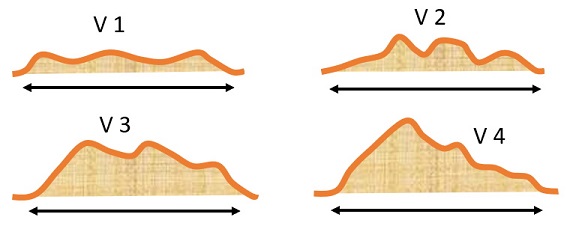
For a handheld, direct, 3D measurement instrument, such as the Peira TM900, the obtained value is independent from the angle or position of the instrument over the tumor. It will not affect the volume output.
The TM900 also stores an optical image in the measurement data base. These together with the tumor shape and all obtained data can easily be traced and consulted afterwards.
Caliper measurement

Using a tumor volume formula
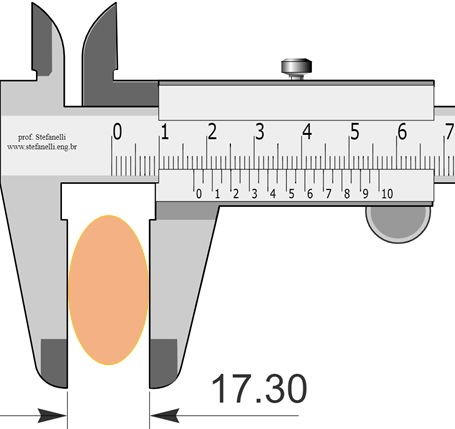
By using a caliper, one will measure width and length of the tumor and then calculate the volume using a standard tumor volume formula, such as π/6 x W x W x L or 1/2 x W x W x L thus assuming a standard and constant shape of the tumor.
During caliper measurements, growth of the tumor in height is not measured and only width and length changes will affect the calculated volume. This results is the loss of information about its real growth.
As illustrated below, with the same measured values for width and length, the calculated volume does not change with the tumor shape.
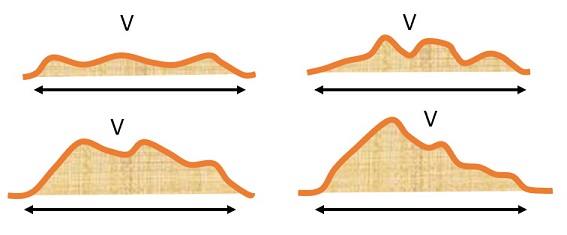
For a caliper measurement, the angle at which it is held over the tumor will affect the obtained value, thus inducing an extra operator and manipulation sensitivity in the results. This effect is illustrated in the included video.
A caliper only digitizes the length and width of the tumor. Further geometrical or visual data are not stored simultaneously.
TM900 3D scanner data, Caliper Measurements and actual tumor volume
Generally, caliper measurements are inaccurate, considerable over estimations of the real tumor volumes. The following document compares tumor volume calculations using caliper measurements to 3D scanner data and estimations of the actual tumor volumes. It shows that the Peira TM900 and its successor the Budetec TM900v2 data are much more realistic and related to reality. Download and view the document at:
https://tumorvolume.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Calipers_TM900_Real.pdf
The following publication is comparing optical 3d measurements with caliper data, which use tumor volume calculations and formula, and luminescence imaging:
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.05.07.592924v1
Measurement time
Peira TM900 and caliper measurement with tumor volume formula are comparable when it concerns the time it takes to do a measurement. For the TM900 one must push the acquisition button and almost immediately the images are stored, and values calculated. The manipulation of the handheld tool is at least as easy as holding a measurement caliper. For both one must have the ease of hand and get used to manipulation of the instrument. Timing wise both methods perform the same.
Measurement method and operator dependency.
When using calipers there is dependency in the measured data of the positioning by the operator of the tool on the xenograft. A direct 3d measurement tool such as the TM900 does not induce such method sensitivity but cannot exclude operator dependency of the obtained values. Both methods cannot avoid variability introduced by the manipulation of the animal. Different operators have diverse ways of holding the animal and tumor while performing the measurement. Even the same operator, with different trials or at different moments in time does not always hold the animal the same way. The tumor can be more and sometimes less visible or express itself from under the skin. That is independent from the use of eighter caliper measurements with tumor volume formula or the Peira tm900.